
Unless you are pouring with self-compacting concrete, the most common way to compact and densify concrete is with an immersion vibrator.
Read on to find out how an electric high frequency vibrator compacts concrete almost two times more effectively than standard flex-drive vibrators.
How do flex-shaft vibrators operate?
Flex-shaft vibrators are by far the most common way to vibrate concrete, they are simple to use, highly portable and relatively inexpensive.
A petrol-powered drive unit provides the drive to the flex-shaft. This shaft rotates a pendulum inside the head of the vibrator creating vibrations. Whilst a relatively simple concept, the engineering inside the head needs to be exact for these units to function correctly.
How do electric high frequency vibrators operate?
Powered by mains power or a generator, high frequency vibrators generate vibrations in a similar way to flex-shaft vibrators. However, unlike flex-drive vibrators, the motor is also housed inside the head of the vibrator. This means that the flex hose between the control box and the vibrator head is simply a power cable.
Understanding vibration
There are two elements that make up vibration - frequency and amplitude.
1 - Frequency
Frequency is simply the number of vibration cycles per minute and is typically represented in VPM or RPM.
Internal vibrators operate at between 8,000 and 17,000 vibrations per minute.
Frequency affects lighter materials such as sand and slurry around the aggregate and is why you will see the aggregate disappear and the slurry liquefy around a vibrator head.
2 - Amplitude
Amplitude is the maximum distance a point on the vibrating head moves from its position of rest.
It affects heavier materials such as aggregate and ultimately determines the radius of influence or action.
To explain amplitude in simple terms, imagine you throw a small rock in a pond. You will see waves moving or expanding from the place you threw the rock. The up and down motion of the waves is the amplitude.

The speed at which these waves travel is the frequency.
If we increase the size or velocity of the rock, the force is increased resulting in bigger waves.
When vibrating concrete, the more stable the amplitude, the more effective the compaction. This is where electric high frequency vibrators have a significant advantage.
Why are electric vibrators more effective than flex-drive vibrators?
This is simply due to the frequency converter built into the electric unit. The convertor converts single phase power into three phase power which results in a more stable vibrator speed under load.
The outcome is a huge increase in the compaction rate per cubic metre.
For example, a 58mm flex-shaft vibrator can compact round 22m3/hour compared to 45m3/h for the same size high frequency electric vibrator.
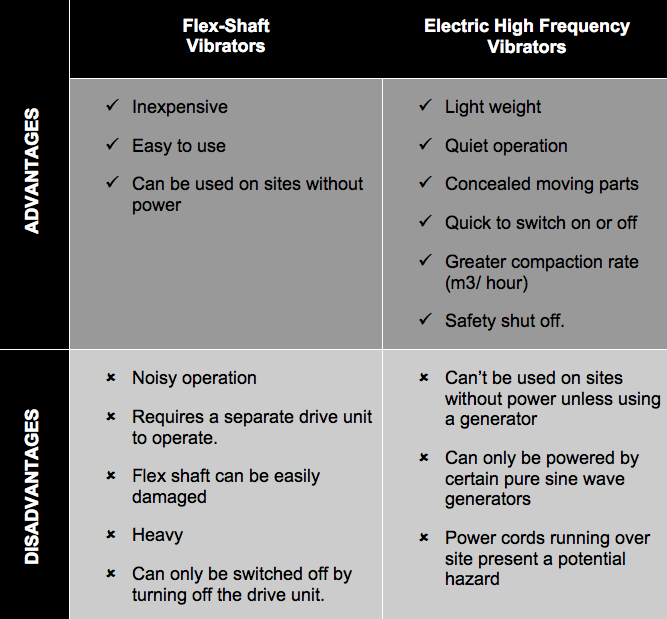
Advantages and disadvantages
Whilst compaction rate is one of the most compelling advantages of electric high frequency vibrators over flex-shaft vibrators, there are also numerous advantages of both flex-shaft and high frequency electric vibrators.
To make it easy, we have summarised them in the below table.
Conclusion
When compiling this article, it was difficult to find concise, easy-to-understand information on the subject. Hopefully we’ve succeeded in clearly explaining the differences between the two so you can decide which is better for your needs.
There is no one-type-fits-all solution. However, we thought that we needed to shed some light on the advantages of high frequency electric vibrators as they can be a secret tool that you can add to your tool kit to gain an advantage over your competition.
Need expert advice on concrete vibrators? Talk to the team at Allcon.
We’re a family business with over 100 years’ collective experience in concrete construction equipment, so we know all the hard truths about concrete.
For more information about concrete vibrators, simply click here to get in touch with us today.
Sources:
Concrete Construction - https://www.concreteconstruction.net/products/general-construction-equipment/finding-the-right-concrete-vibrator_o
NCPA - https://precast.org/2010/05/the-proper-use-of-vibrators/
